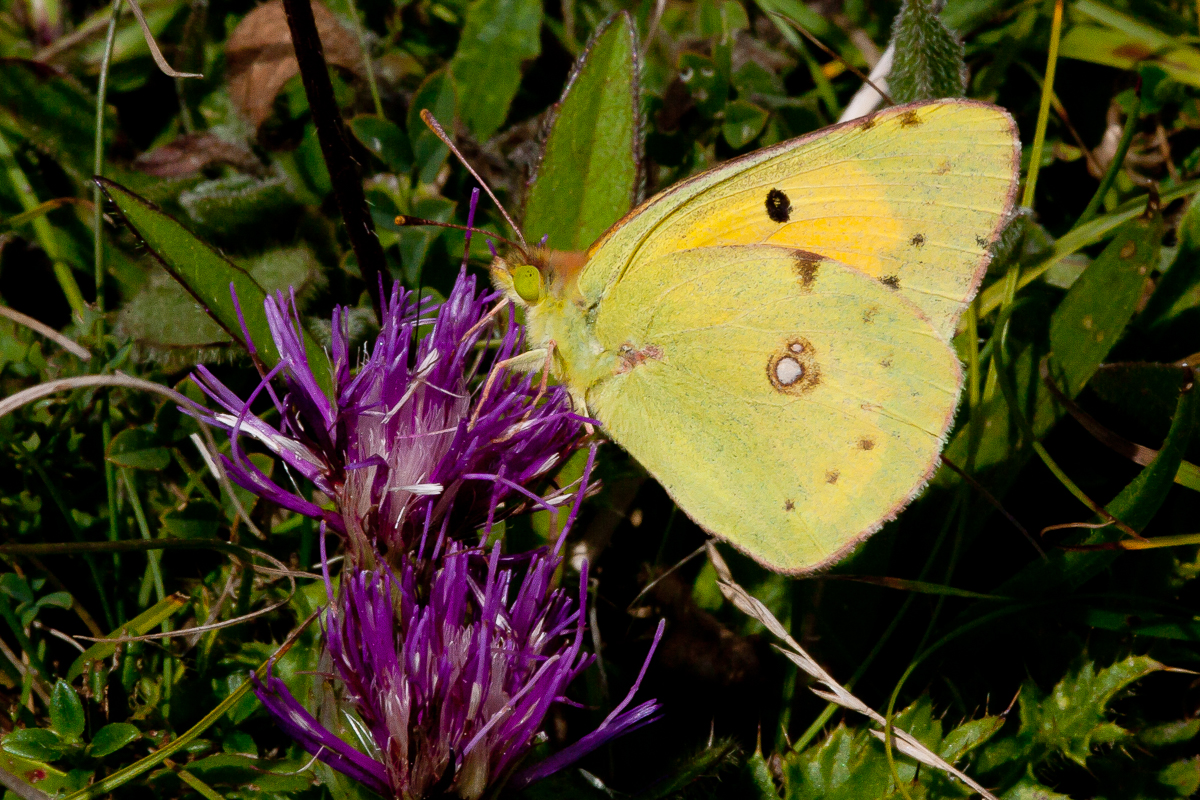
Photo © Peter Eeles
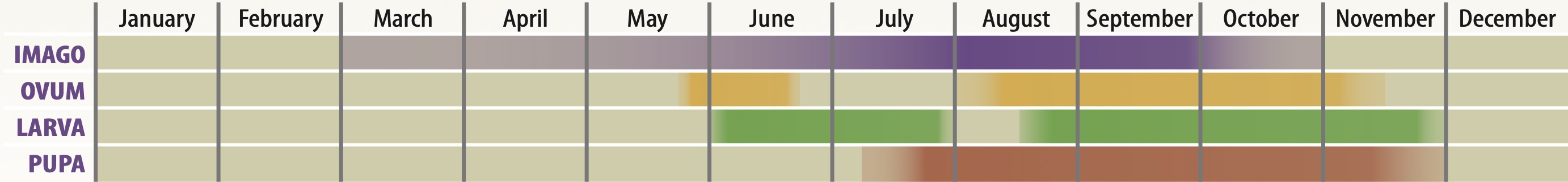
The Clouded Yellow is primarily an immigrant to the UK, originating from north Africa and southern Europe, with numbers varying greatly from year to year - an estimated 36,000 butterflies appearing in one of the infrequent "Clouded Yellow" years in 1947. In more recent years, it has been shown that this species has successfully overwintered in the south of England. However, it is believed that the majority of individuals perish, since both larva and pupa of this continuously-brooded species are easily killed by damp and frost. In good years this species can produce up to 3 generations in the UK. In flight, this species is often mistaken for one of the commoner "whites", but the orange-yellow colour is quite distinctive, even in flight, and unlike any other species. The Clouded Yellow has a distribution befitting a highly-migratory species, and can be found anywhere in the British Isles. Many immigrants remain near the coast where they feed, mate, and lay eggs. Others disperse inland and this species is found in both Scotland and Ireland in good years.
This strong-flying butterfly always settles with its wings closed and so the dark borders on the uppersides of the wings are only visible when in flight. There is no elaborate courtship and, having mated, the female is subsequently able to lay an extraordinary number of eggs - up to 600 have been recorded from a single female.
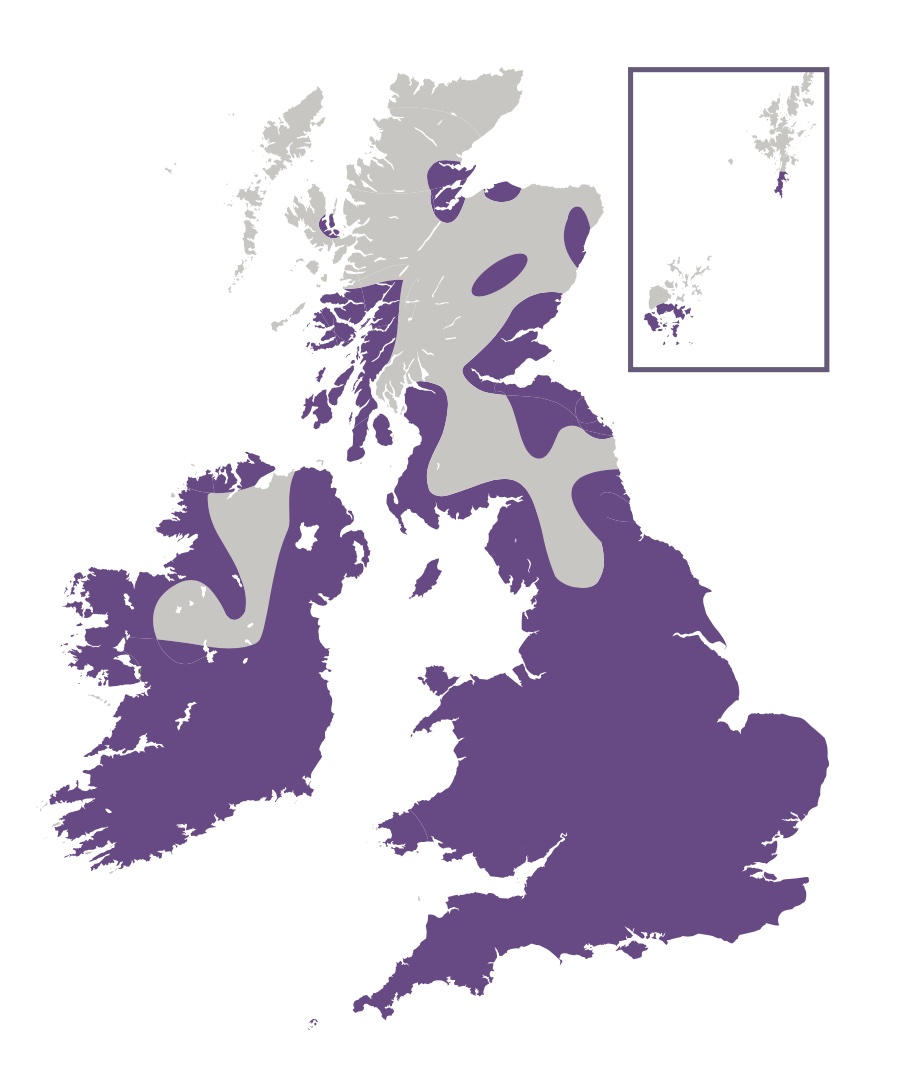
This butterfly can be found in just about any open habitat in the countryside, including coastal cliffs, open downland, and fields containing the larval foodplants of Clovers, Lucerne and Bird's-foot Trefoil.
Adults feed primarily on Common Fleabane (Pulicaria dysenterica), dandelions (Taraxacum spp.), knapweeds (Centaurea spp.), ragworts (Jacobaea spp.), thistles (Carduus spp. and Cirsium spp.), vetches (Vicia spp.) and Wild Marjoram (Origanum vulgare).
The primary larval foodplant is clovers (Trifolium spp.). Common Bird's-foot-trefoil (Lotus corniculatus) and Horseshoe Vetch (Hippocrepis comosa) are also used.