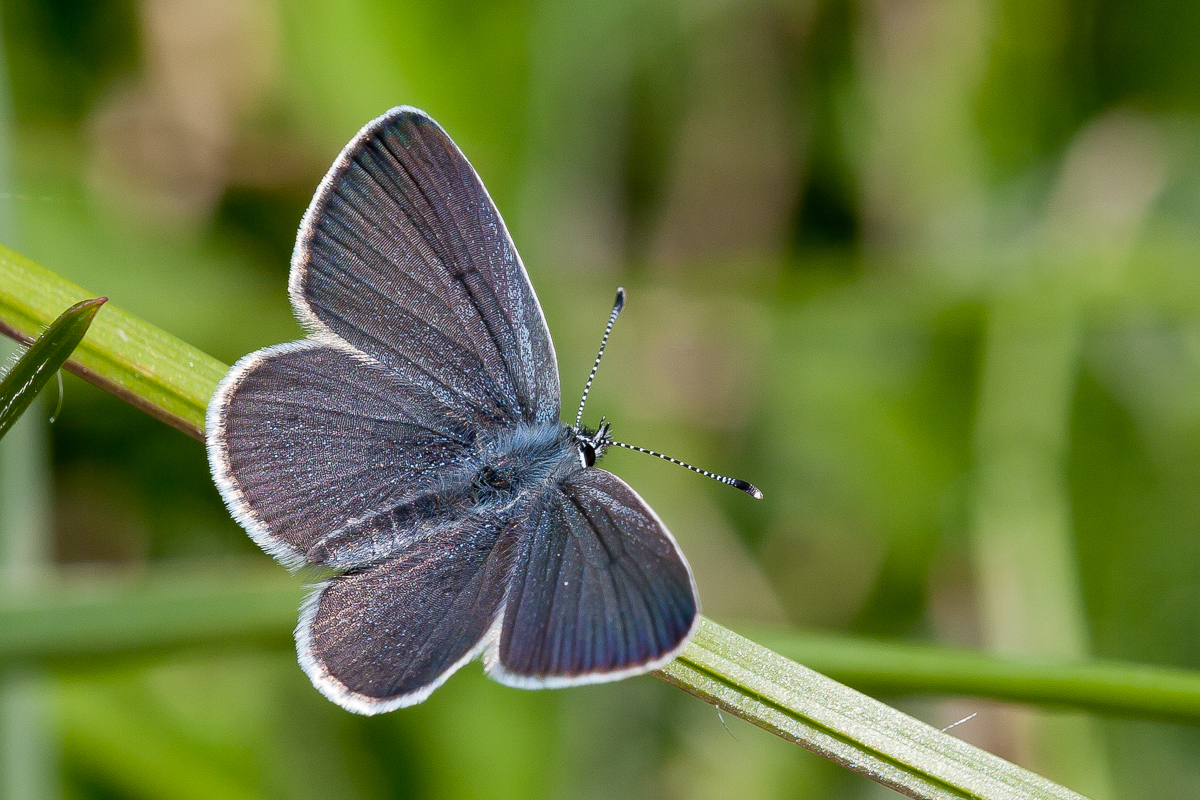
Photo © Peter Eeles
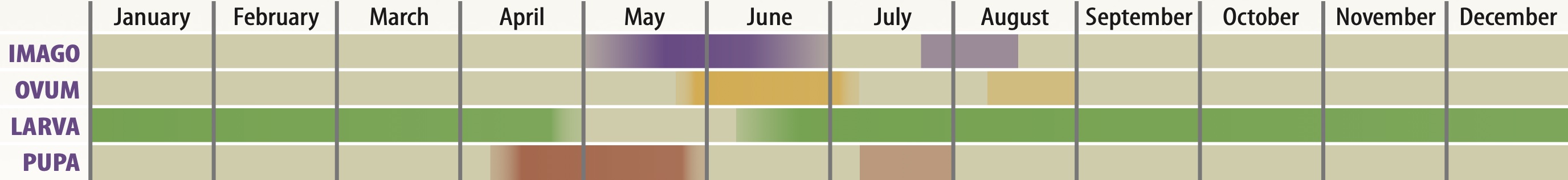
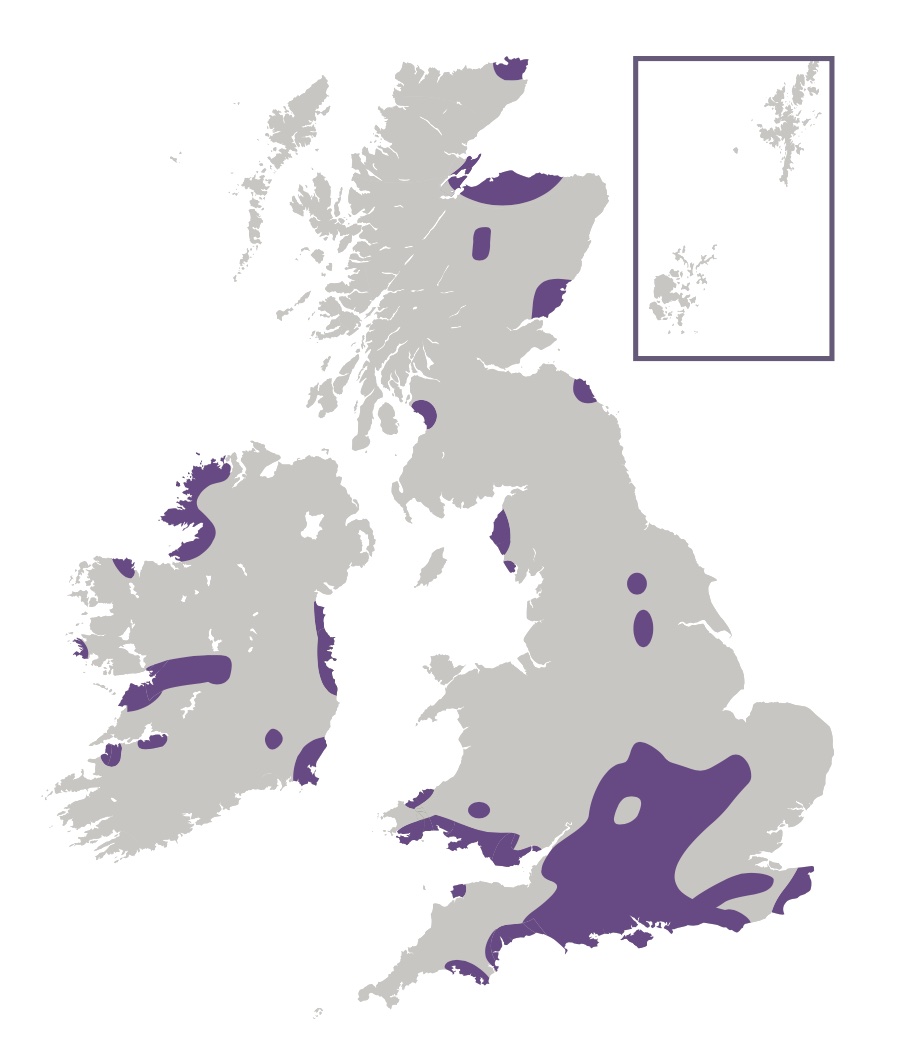
This is our smallest resident butterfly with a wing span that can be a little as 16mm. The sexes are similar in appearance, although the male upperside is almost black with a dusting of blue scales, whereas the female is more dark brown in colour. Both sexes have an underside that is silvery-grey in colour, and not unlike that of the Holly Blue. This butterfly has a large distribition, being found from northern Scotland to the south of England, with colonies also in Wales and Ireland. However, outside of its strongholds in the south of England, colonies are often isolated pockets, typically in coastal locations. Most colonies consist of less than 30 adults, although a few colonies consist of thousands of adults. This butterfly is absent from the western and northern Scottish isles, the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands.
Both sexes spend a large amount of time basking or resting. Males perch on small shrubs or grass stems which they leave when investigating passing insects or when searching out nectar sources. They are not territorial, however, and can often be found in small groups of 2 or 3. Both sexes take nectar from various flowers, with Kidney Vetch, Bird's-foot Trefoil and Horseshoe Vetch being particular favourites. Males will also take salts and minerals from damp mud, animal droppings and carrion.
Virgin females entering the perching sites are quickly mated without any elaborate courtship. Once mated, the female spends most of her time searching out suitable plants on which to lay and, once found, she lays a single egg between 2 florets on the flower head. She then rubs her abdomen over the flower head which is believed to deter other females from laying on the same plant since the larvae are cannibalistic in their first instar.
Suitable sites for this species are those that are sheltered and contain a good amount of Kidney Vetch, together with grasses and shrubs which are used for perching and roosting. A wide variety of habitats is used, including unimproved chalk and limestone grassland, abandoned quarries, road and railway embankments and woodland rides and clearings.
Adults feed primarily on Common Bird's-foot-trefoil (Lotus corniculatus), Horseshoe Vetch (Hippocrepis comosa) and Kidney Vetch (Anthyllis vulneraria).
The primary larval foodplant is Kidney Vetch (Anthyllis vulneraria).