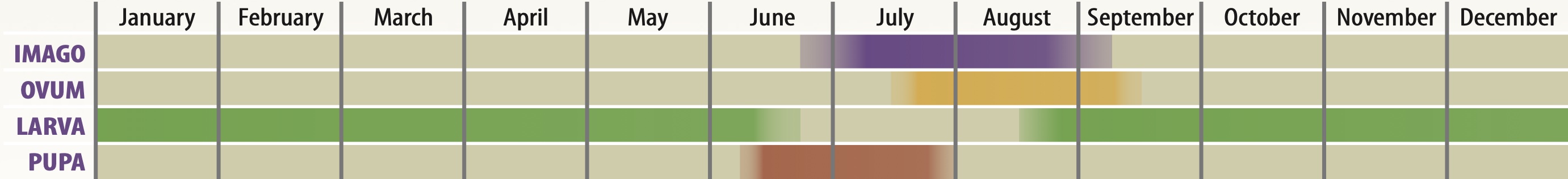
Photo © KEC
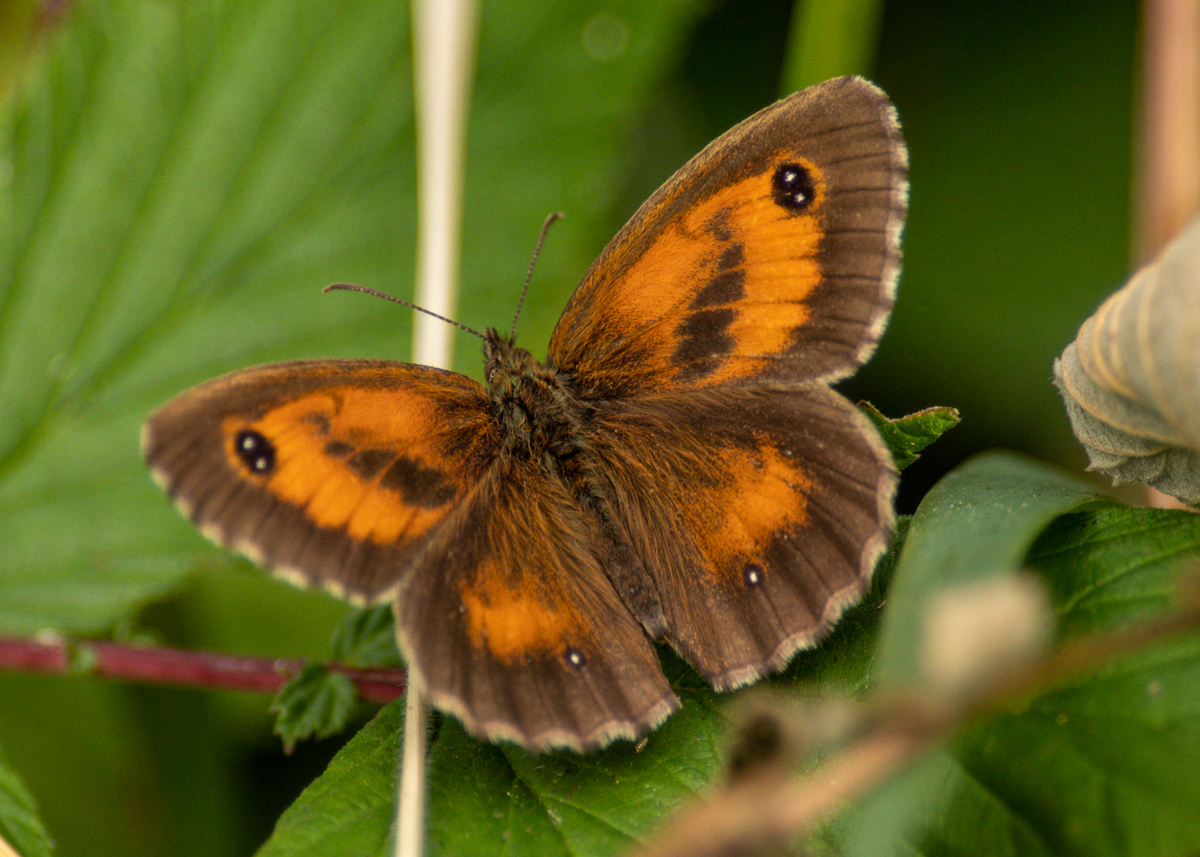
The Gatekeeper, also known as the Hedge Brown, is a golden butterfly that provides a welcome sight in the middle of summer, when the fresh adults start to emerge. This butterfly spends much of its time basking with wings open, when the sexes are easy to tell apart - only the male has the distinctive sex brands on the forewings. In England and Wales this common and widespread species is found south of a line between Westmorland in the west and South-east Yorkshire in the east. In Ireland it is confined to coastal areas of the south and south-east counties. The butterfly is also found in the Channel Islands, but is absent from Scotland and the Isle of Man. The habitat this butterfly requires is found over most of the British Isles, and so we can only assume that the restriction to its range is governed primarily by climate. Colonies vary greatly in size, depending on the available habitat, ranging from a few dozen individuals to several thousand.
Males set up small territories, often centred on a particular shrub or bush, and will fly up from their perch to investigate passing butterflies in the hope of finding a mate. Pairing occurs without any obvious courtship and, once mated, a female will typically lay between 100 and 200 eggs.
Although both sexes feed from honeydew, they will also feed from whatever nectar sources are available - Bramble and Ragwort being particular favourites.
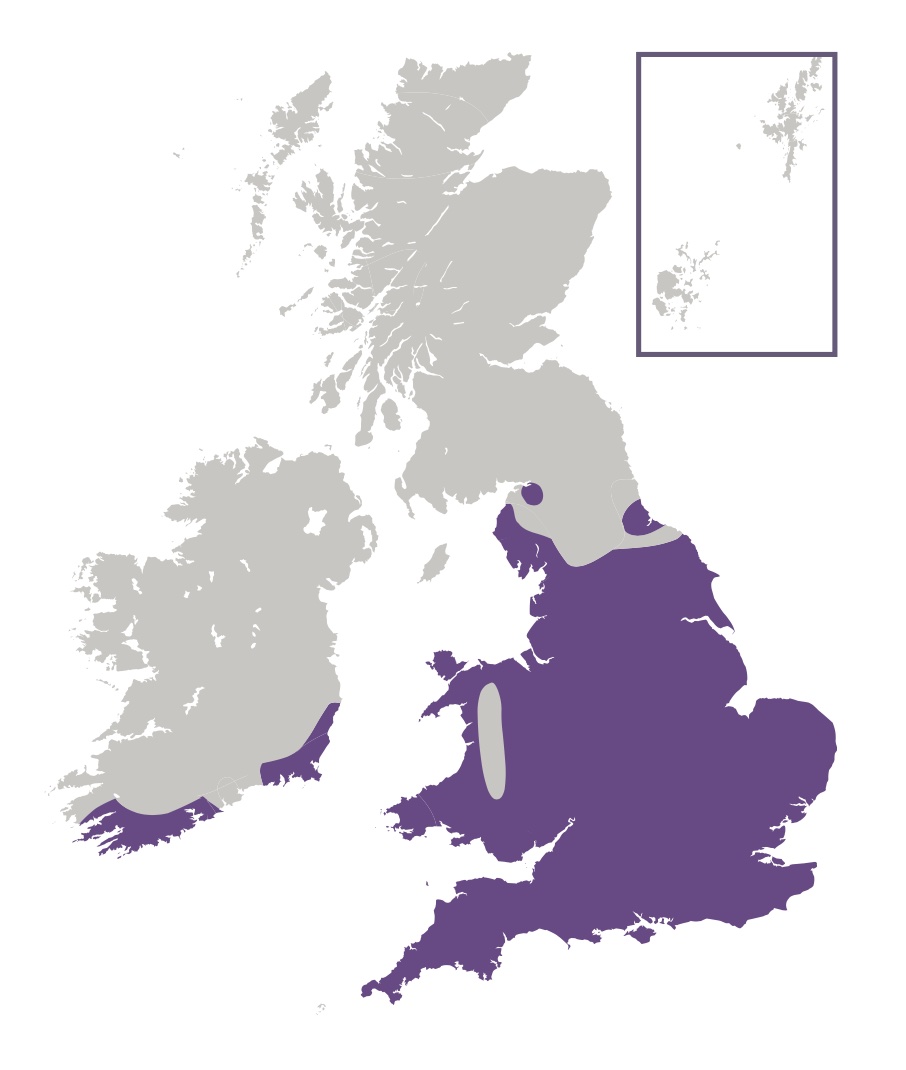
This species can be found wherever shrubs grow close to rough grassland. In fact, some of the largest colonies can be found at field edges and along hedgerows and we can expect to find this butterfly in scrubby grassland, woodland rides, country lanes, hedgerows and the like anywhere within its range.
Adults feed primarily on brambles (Rubus spp.), Common Fleabane (Pulicaria dysenterica) and ragworts (Jacobaea spp.). Devil's-bit Scabious (Succisa pratensis), Hemp-agrimony (Eupatorium cannabinum), Red Clover (Trifolium pratense), thistles (Carduus spp. and Cirsium spp.), Water Mint (Mentha aquatica), Wild Privet (Ligustrum vulgare) and Wild Thyme (Thymus drucei) are also used.
The primary larval foodplants are bents (Agrostis spp.), fescues (Festuca spp.) and meadow-grasses (Poa spp.).